深入理解 VMware Workstation 虚拟网络:理论篇
坑边闲话:ESXi 的虚拟网络是非常符合现实世界的直觉的,相对而言,我本人认为 ESXi 的网络比 VMware Workstaion Pro 的网络要更加简单纯粹。但 VMware Workstaion Pro 因属于 Type-II 型虚拟机监视器,所以具有一些 ESXi 所提供不了的功能。此外 VMware Workstaion Pro 是在宿主机上运行,因此在某些个人 PC、工作站上也能发挥很好的功用。
这篇文章将详细介绍 VMware Workstaion Pro 16 的虚拟网络。
1. VMware 虚拟网络编辑器·
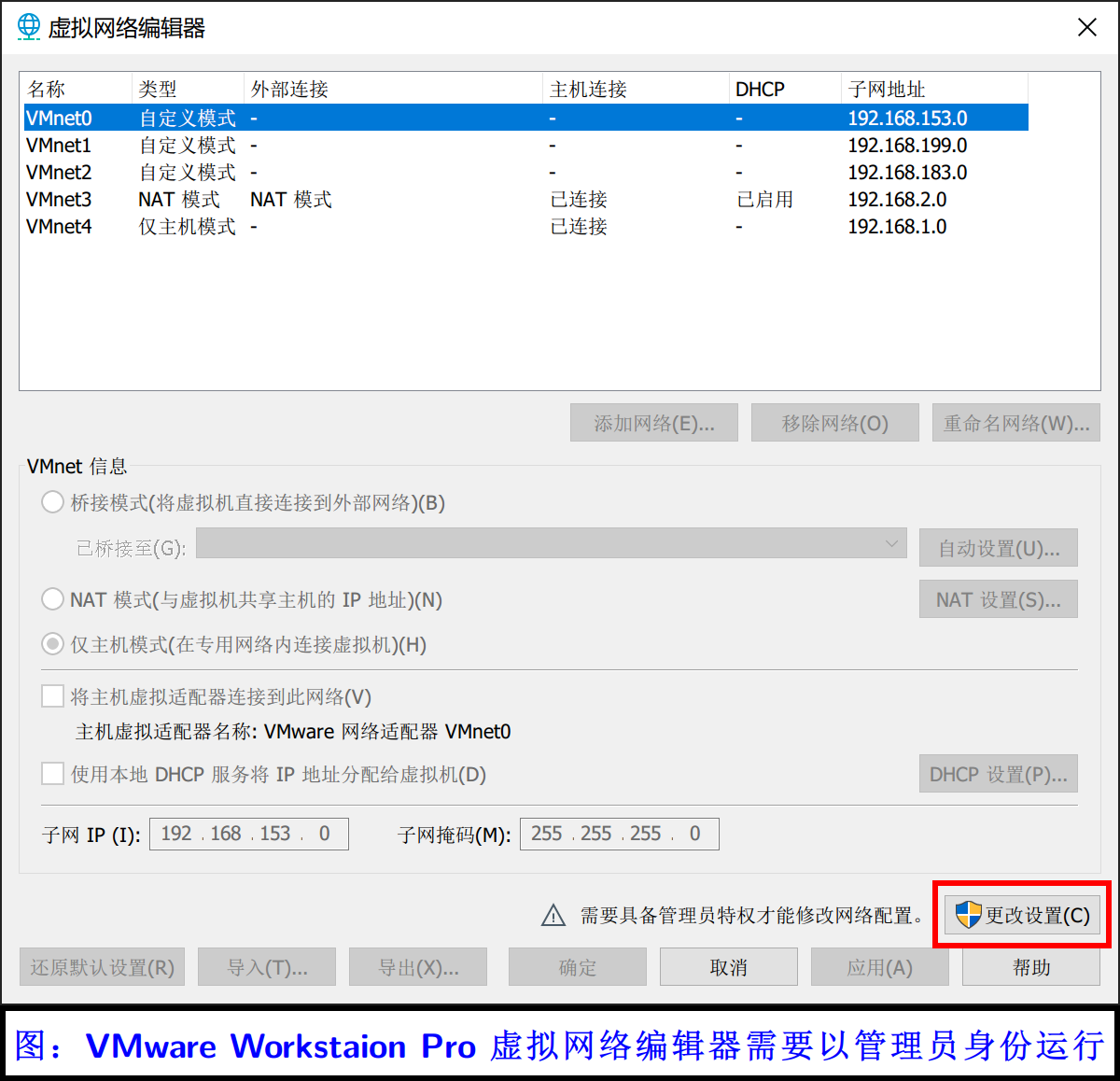
点击带有管理员权限图标的“更改设置”,即可看到当前的虚拟网络配置。
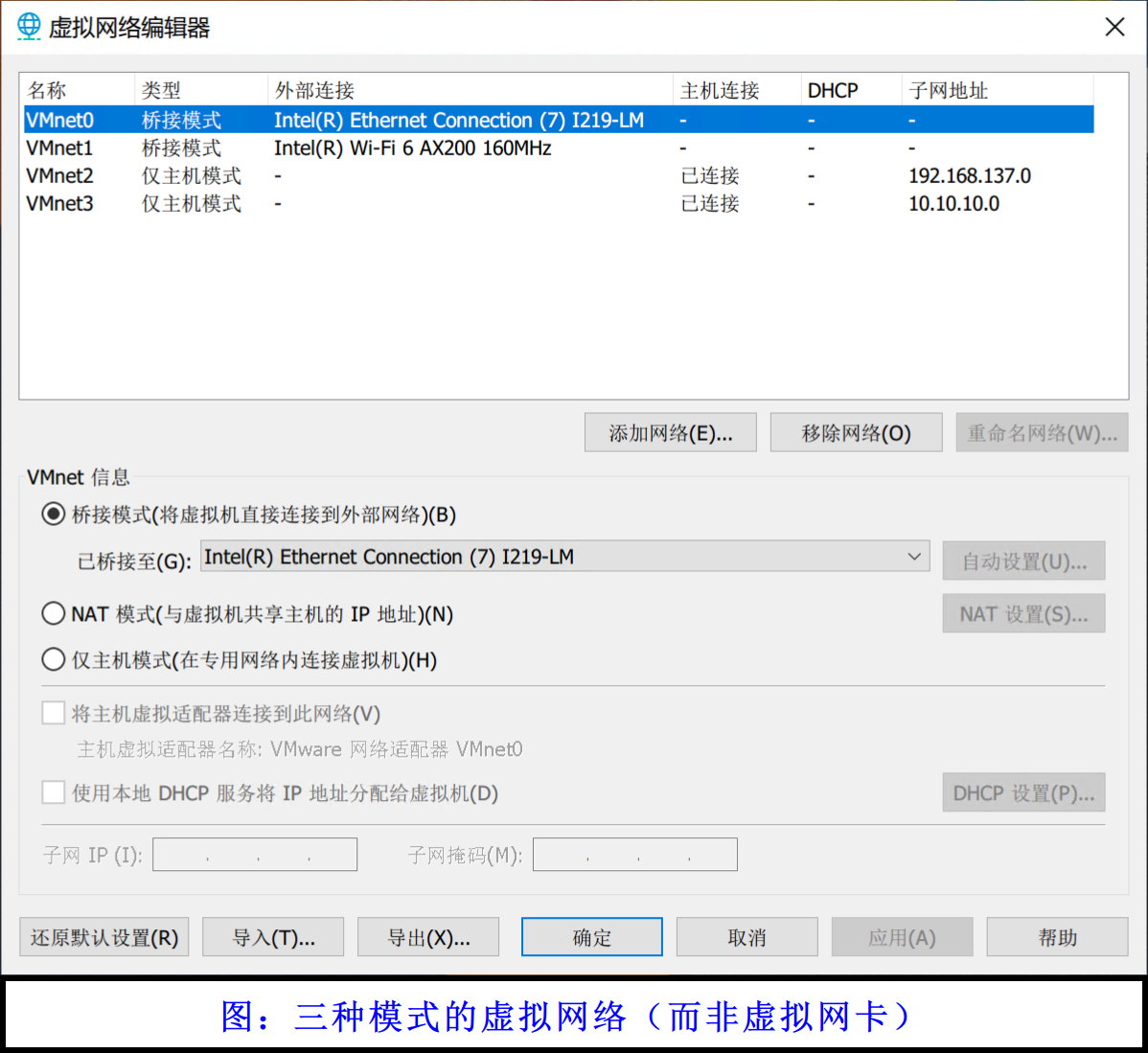
在 VMnet 信息中可以选择将选中的网络设置为三种类型:
- 桥接模式(Bridged Networking)
- NAT 模式(Network Address Translation)
- 仅主机模式(Host-Only Networking)
关于这三种模式的官方介绍,参见:https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-Workstation-Pro/16.0/com.vmware.ws.using.doc/GUID-0CE1AE01-7E79-41BB-9EA8-4F839BE40E1A.html
我个人认为官方画的图并不是很适合新手理解,这里我就借助一些简单的实验深入讲解一下。
1.1 桥接模式(VMnet0)·
官方解释:
Bridged networking connects a virtual machine to a network by using the network adapter on the host system. If the host system is on a network, bridged networking is often the easiest way to give the virtual machine access to that network.
Bridged networking configures the virtual machine as a unique identity on the network, separate from and unrelated to the host system. The virtual machine is a full participant in the network. It has access to other machines on the network, and other machines on the network can contact it as if it were a physical computer on the network.
桥接模式的虚拟网络的数量是受限的,需要小于等于物理网卡的数量。因为一个桥接的网络必须有一个对应的物理网卡。
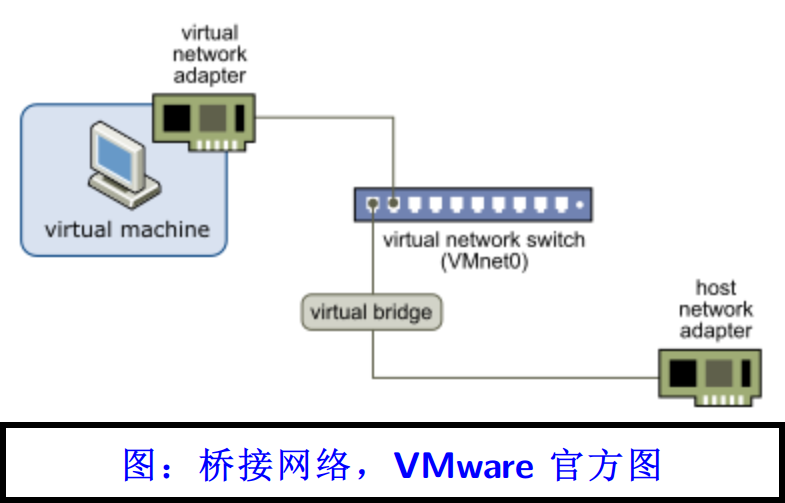
桥接网络其实也不太好理解,毕竟很难想象有这么一台虚拟交换机。我们更倾向于认为桥接就是直接套用了物理网卡,所以虚拟机和宿主机之间通信都需要通过外面的物理交换机。但是事实真的如此吗?
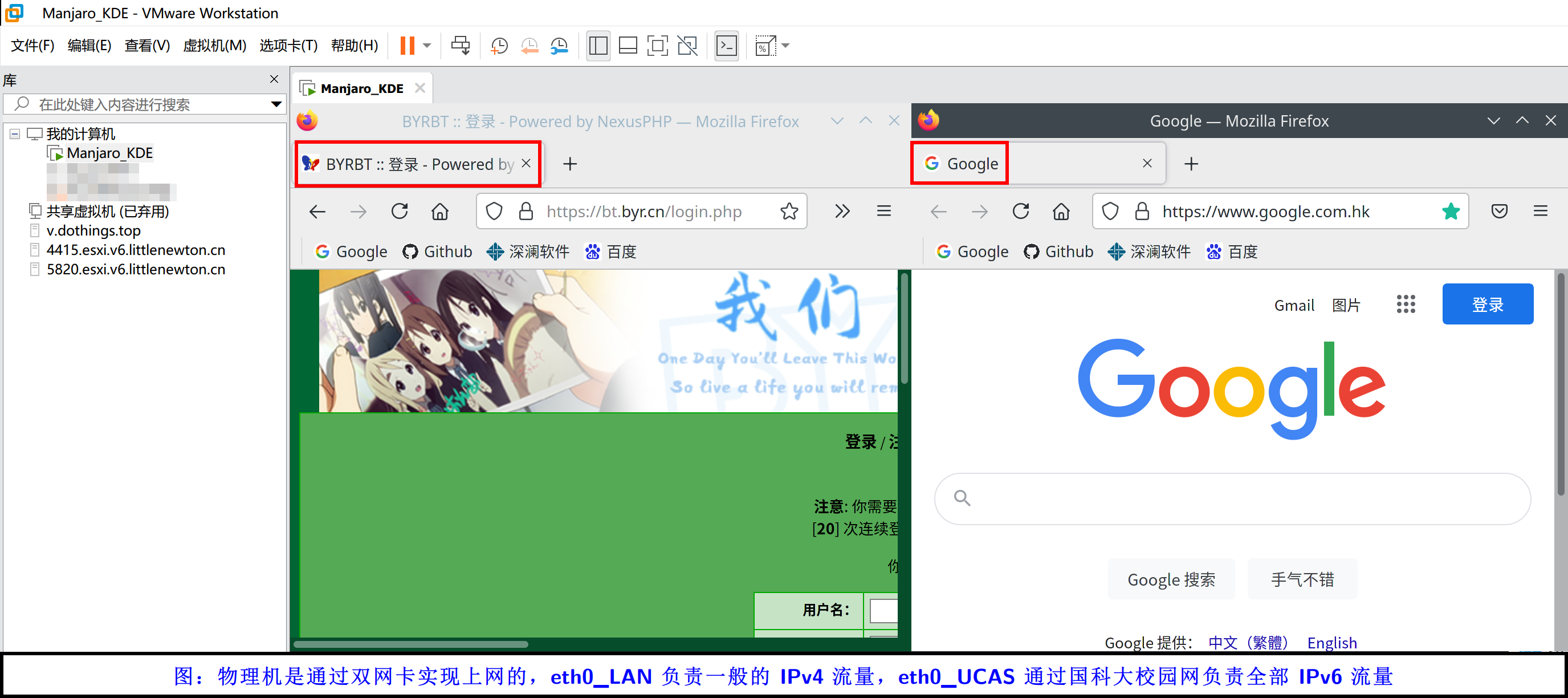
并不是。做个简单的实验,我们在宿主机上开一个 SMB 共享,在虚拟机里访问这个共享文件夹,并拷贝东西出来。
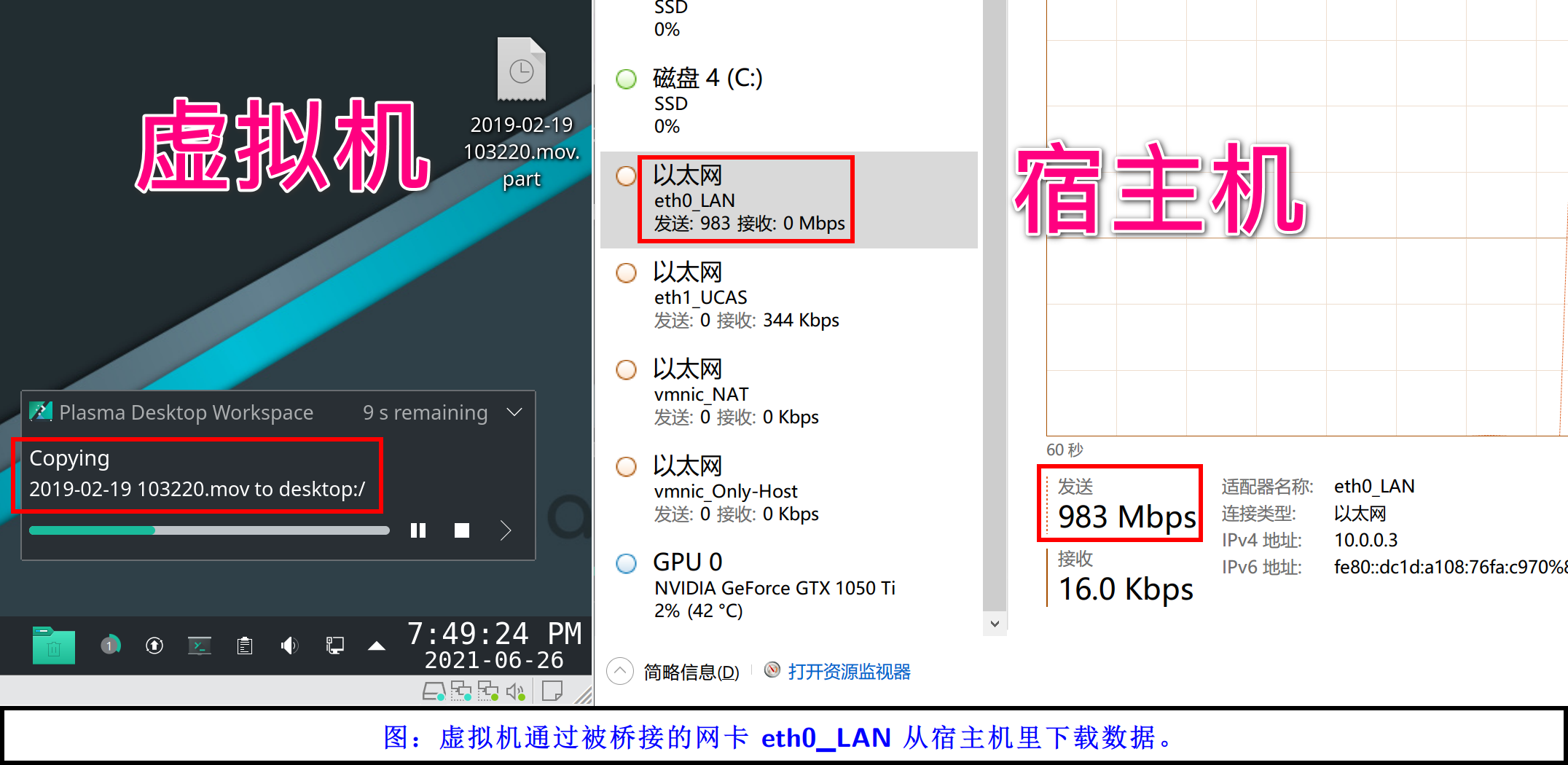
在上图中可以发现,桥接模式下宿主机和虚拟机之前传输文件,应该是宿主机上传、虚拟机下载,然后网卡的上行、下行应该跑满。但是事实并非如此。eth0_LAN 这个网卡只有发送,但是没有接收。所以桥接网络的内部交换机模型确实是官方描述的那样。不过我依旧认为那种描述是不够的,我倾向于认为 VMware 的软件复用的被桥接网卡的物理层和链路层,在开启了桥接模式之后,你插入被桥接网卡的网线,就相当于插入了官图中的交换机,而你的物理网卡也插入了这台物理交换机。所以虚拟机从宿主机里下载文件时,宿主机的网卡会跑满上行,但是虚拟机这一边是用的内存直接拷贝,所以宿主机的网卡看不到下行的网速。
综上,桥接网络里,也是存在虚拟交换机的!
1.2 NAT 网络(VMnet8)·
官方解释:
The host system has a virtual network adapter on the NAT network. This adapter enables the host system and virtual machines to communicate with each other. The NAT device passes network data between one or more virtual machines and the external network, identifies incoming data packets intended for each virtual machine, and sends them to the correct destination.
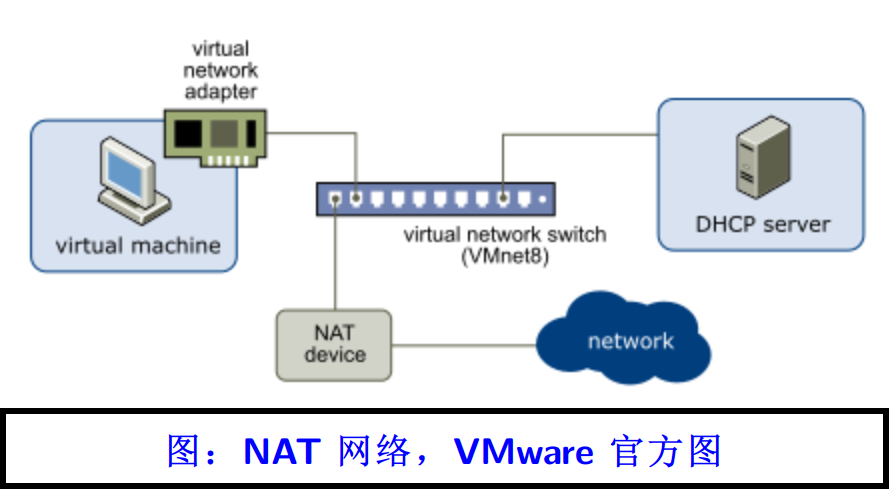
到了 NAT 网络,情况就与 Host-Only 模式截然不同了。情况变得复杂了很多,而且有些设备是你看不到的。
NAT 网络是一种非常高级的网络。读者最好有 NAT 的相关知识基础。
VMware Workstation 的 NAT 网络配置好之后,软件会在你的网络适配器里添加一个虚拟网卡,同时创建一个虚拟的交换机。你的宿主机通过前面提到的虚拟网卡接入虚拟交换机。如果这个 NAT 网络开启了 DHCP 服务,而且这个宿主机的虚拟网卡被配置为了 DHCP 客户端模式,那么它将获得一个 IP 地址。
NAT 服务器一般是由网关担任。VMware 官方的 NAT 拓扑图大概是有些表达上的问题,因为这个“NAT device”到底是什么它没说清楚。
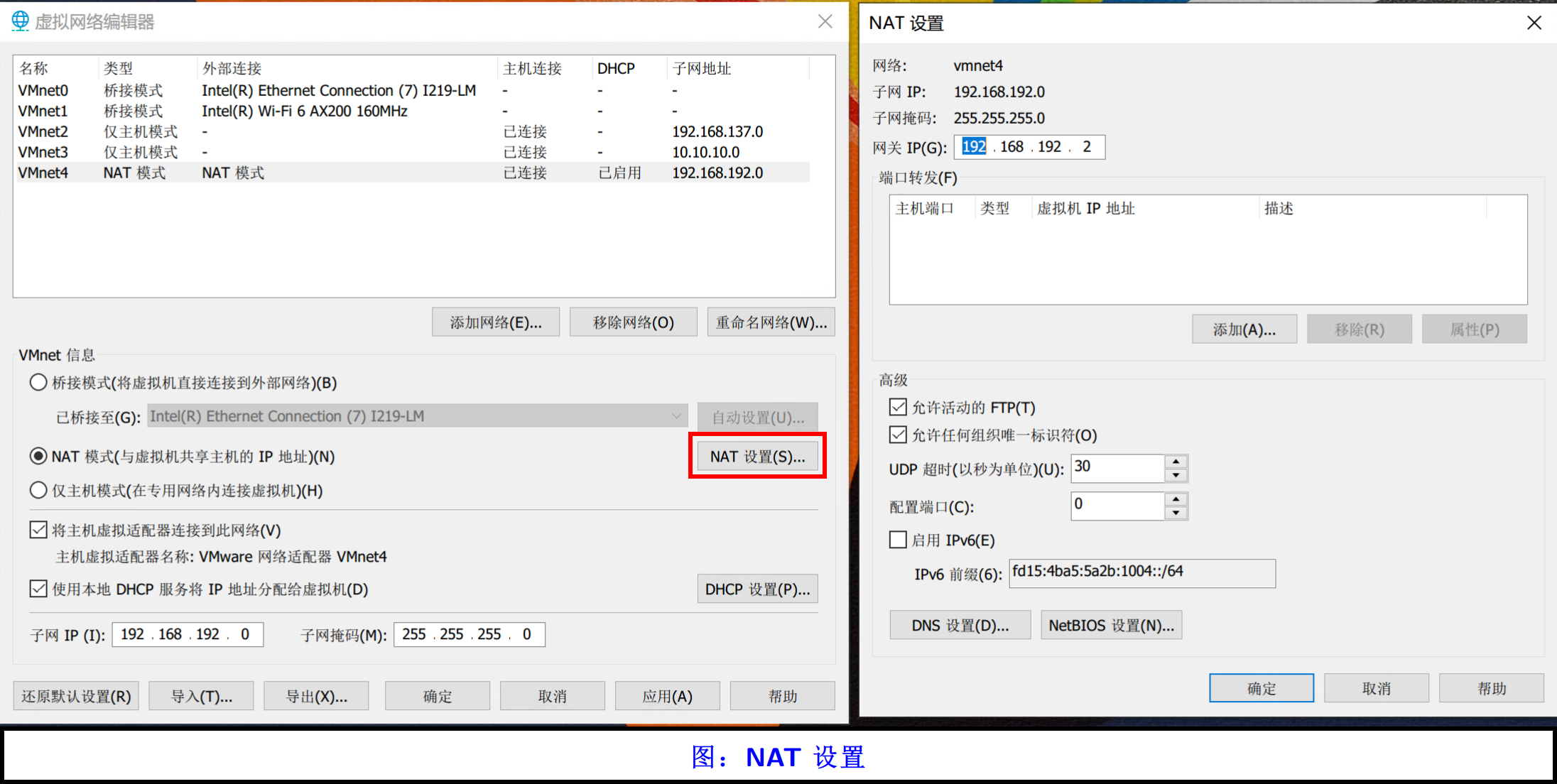
打开 NAT 设置,可以看到软件提供了一个网关的 IP 地址配置项。所以 VMware 官方图中的 NAT device 指的就是某个以 192.168.192.2 为 LAN 侧 IP 的虚拟设备,这个设备可以通过某个服务实现 NAT 功能。换句话说,虚拟网络中不仅有你的虚拟机,还有许多“幽灵”,这些“幽灵”设备你看不到,但是他们会默默为你提供服务。在配置了网关的 IP 之后,如果宿主机能够上网的话,那么虚拟机们也就可以上网了。大概流程是这样的:
- 虚拟机 VM1 想访问 baidu.com,于是它发起连接请求
- 请求包中的发送方信息在局域网里通过 MAC 地址查询,被发送到网关设备 NAT device
- NAT device 按照宿主机的路由策略对虚拟机的内网地址进行针对性修改。
接下来解释什么是“针对性修改”。
这里重点说明,为什么 NAT 配置是非常高级的。首先,我们的宿主机可能有多个网卡,多个网卡按照我们自己配的路由表进行独立的网络流量路由。有的网卡连接到校园网,有的网卡连接到外网(如哔哩哔哩、Youtube 等),有的网卡直连到 NAS 服务器。这个时候,NAT device 要决定数据包的发送地址要被如何改写,所以大致应该进行如下查询:
- 查看数据包的目的地址,通过物理机操作系统的路由表中 NextHop 信息决定要通过物理机的哪个 Interface 转发出去;
- 根据 1 提供的 Interface,NAT device 将 VM1 的发送地址由 NAT 内网地址修改为宿主机对应的 Interface 的 IP 地址。
这里举个例子说明一下。我的宿舍主路由因为校园网地址分发问题,并没有直接接入 IPv6,所以我的路由器是无法访问 IPv6 地址的(但是可以访问谷歌)。但是我的这台演示电脑却可以通过一个直连校园网的网卡直接访问 IPv6. 在 VMware NAT 网络下的虚拟机,既可以访问谷歌,也可以访问 IPv6 网站。这足以说明我对 NAT device 的地址翻译策略的理解是正确的。
1 | # 我的路由配置 |
1.3 仅主机模式(VMnet1)·
官方解释:
Host-only networking is useful if you need to set up an isolated virtual network. In a host-only network, the virtual machine and the host virtual network adapter are connected to a private Ethernet network. The network is completely contained within the host system.
The network connection between the virtual machine and the host system is provided by a virtual network adapter that is visible on the host operating system. The virtual DHCP server provides IP addresses on the host-only network.
In the default configuration, a virtual machine in a host-only network cannot connect to the Internet. If you install the proper routing or proxy software on the host system, you can establish a connection between the host virtual network adapter and a physical network adapter on the host system to connect the virtual machine to a Token Ring or other non-Ethernet network.
On a Windows host computer, you can use host-only networking in combination with the Internet Connection Sharing feature in Windows to allow a virtual machine to use the dial-up networking adapter or other connection to the Internet on the host system.
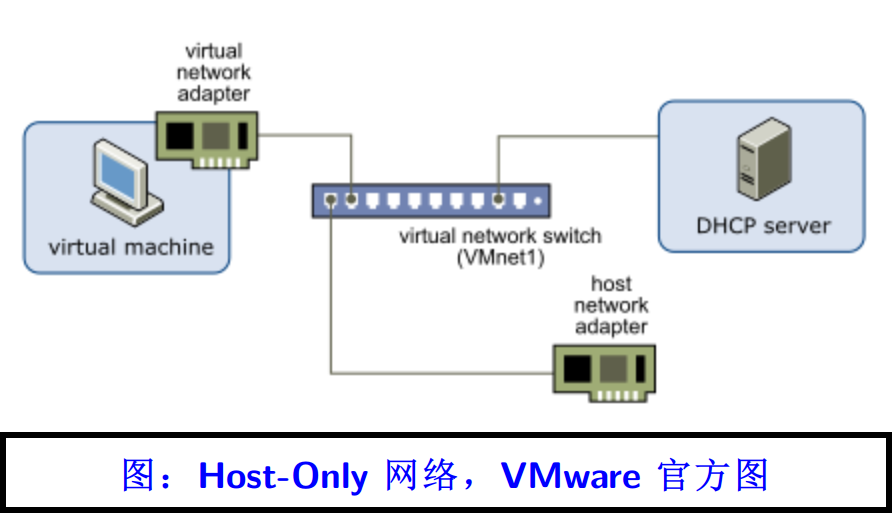
仅主机模式就非常简单暴力了,它会完成三个操作:
- 创建一个虚拟交换机,并在网络中布置一台虚拟的 DHCP server 提供服务
- 给宿主机分配一个虚拟网卡,把这个虚拟网卡接入这台虚拟交换机
- 分配了仅主机模式的虚拟网卡,也将通过这个虚拟网卡接入该虚拟交换机
仅主机模式就非常好理解了,原则上仅主机模式是不能让虚拟机上网的,仅能与主机通信。但是我们可以通过配置 Windows 的 Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) 服务,让主机的那张虚拟网卡成为 Host-Only 交换机的上行链路,这样就能变相实现虚拟机访问 Internet 乃至其他网络。
但是通过上述手动配置的方法与 NAT 虚拟网络还是有很大不同的。 NAT 更加高级,可以套用系统的路由策略,使得你的虚拟机就像你的物理机一样访问所有能访问的网络。做了 ICS 的仅主机模式网络,其中的虚拟机也仅仅能访问提供了 ICS 的那张网卡所能访问到的网络。所以二者的区别非常明显!
总结·
本文详细介绍了 VMware Workstation 的三种网络配置,并纠正了许多朋友经常存在的认知误区。
希望对大家有所帮助!




